Innovation in Soccer: Study and Implementation of Protective Masks through 3D Printing
3D Printing in the Development of Sports Protective Devices
Simone Gallozzi Demonstrates Its Potential in His Thesis
Sport and 3D Print
The world of sports is constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance athletes’ performance, reduce the risk of injuries, and facilitate recovery.
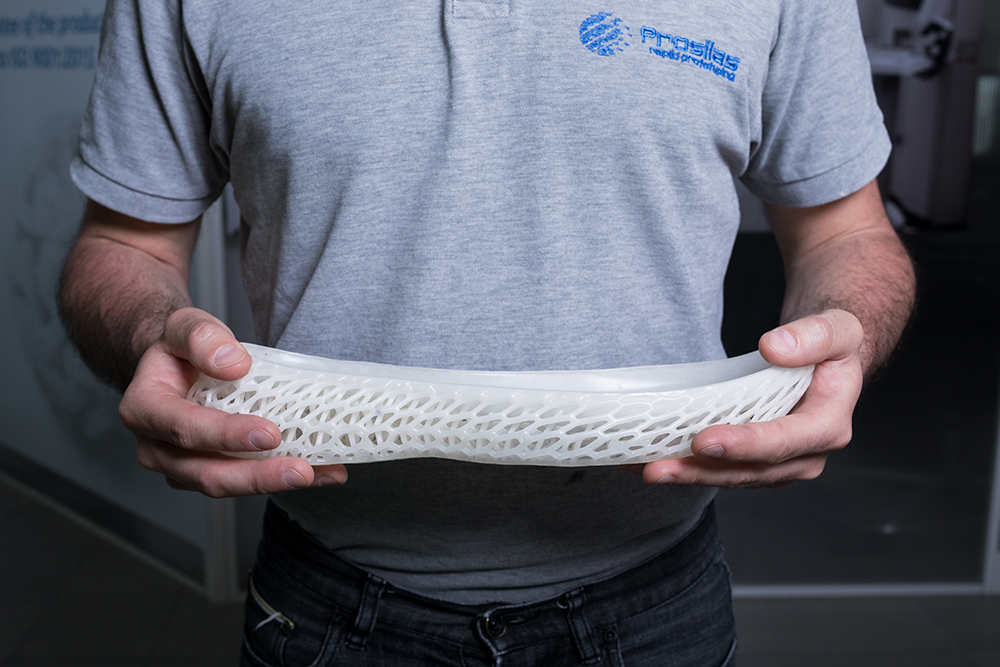
3D printing, in particular, is emerging as an increasingly popular technology, enabling the production of customizable protective devices such as prosthetics, running shoe soles, helmets, and other safety gear – as exemplified by our Case Study on Lube Volley.
In particular, Simone Gallozzi’s thesis demonstrates the feasibility and details the workflow of a 3D printing application in the field of soccer
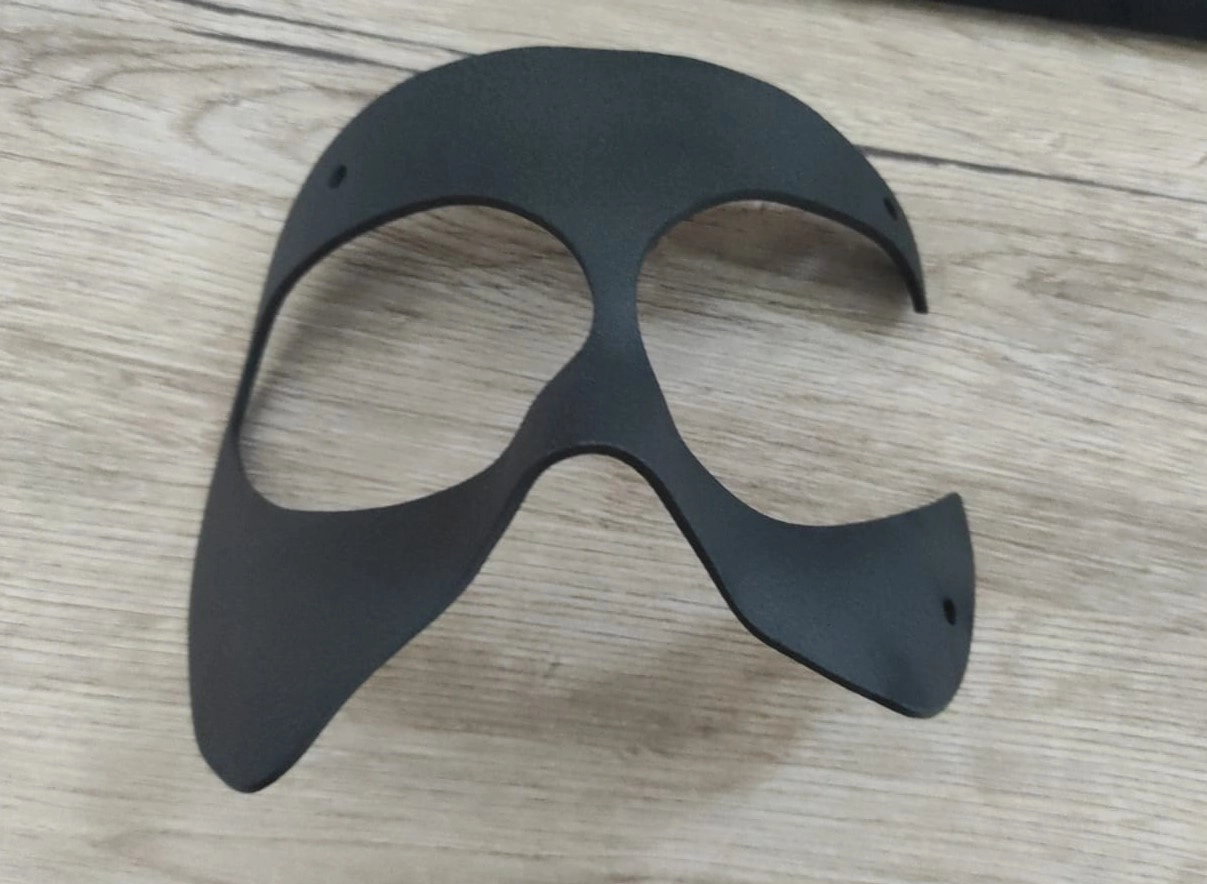

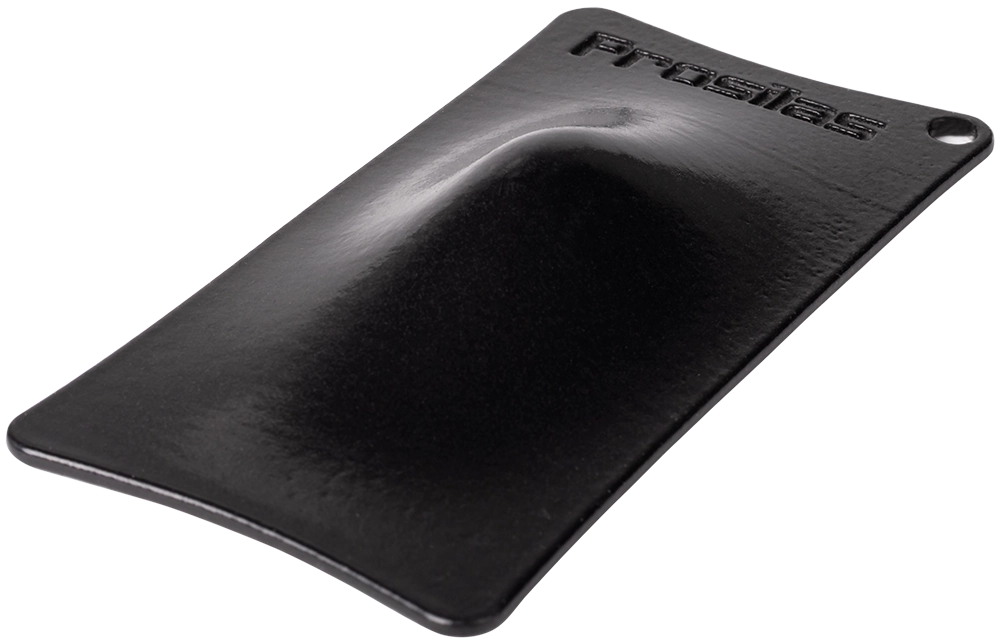
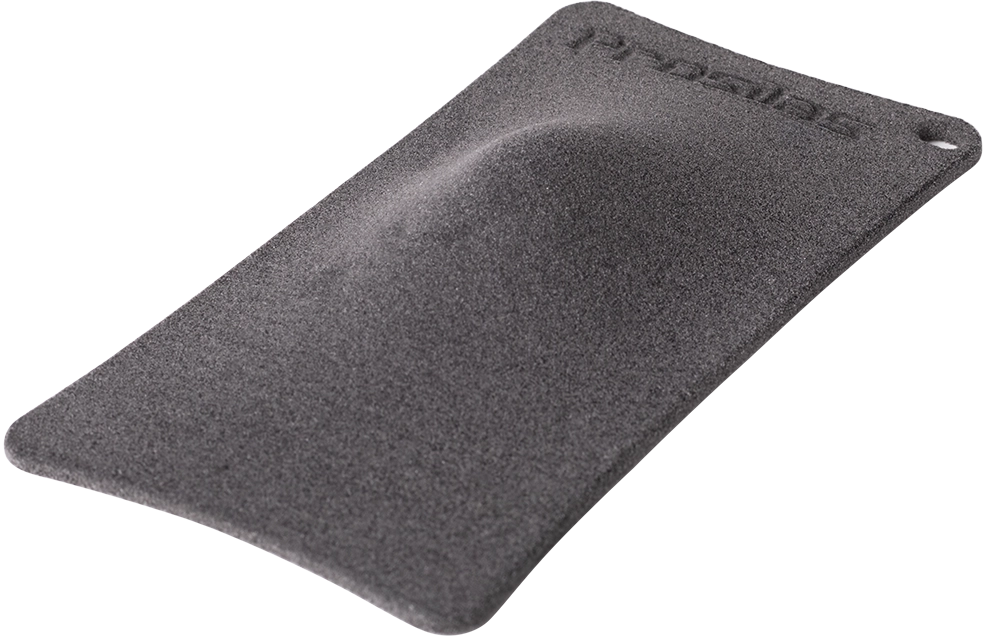
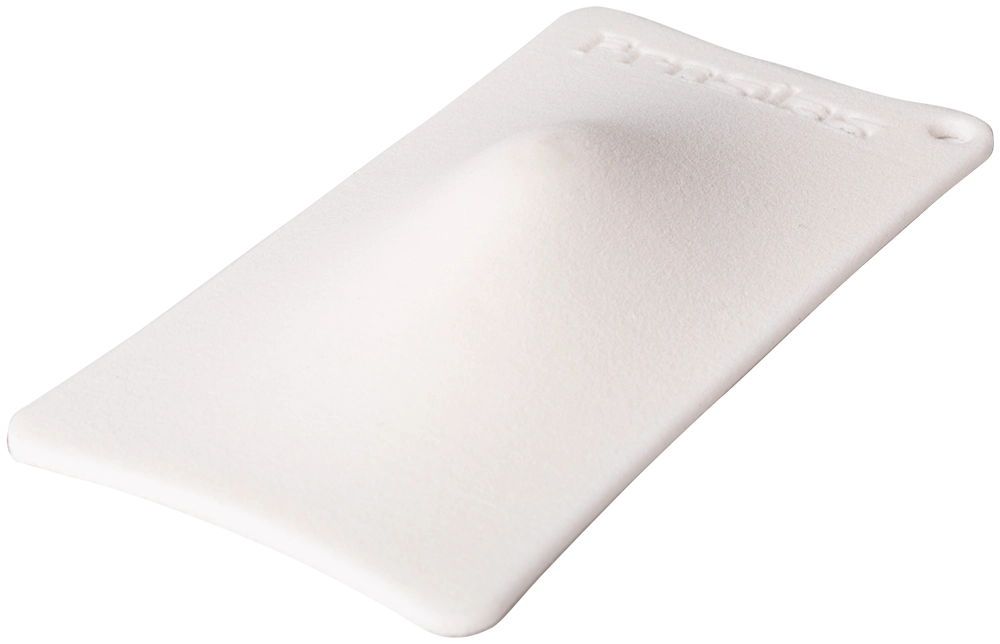
Simone Gallozzi protective mask in PA 603 CF
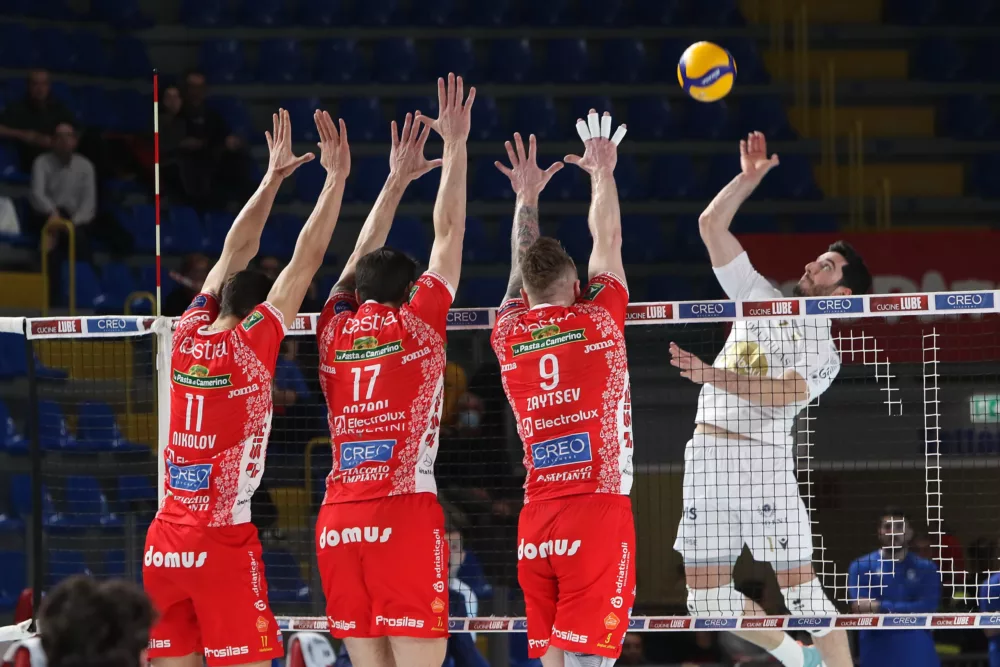

Lube Volley Athletes
The candidate, in his thesis titled ‘ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING IN THE SPORTS WORLD – Analysis and Production of Facial Protective Masks in Soccer,’ under the guidance of Professor Eleonora Santecchia, conducted a thorough analysis on the application of 3D printing in sports.
His main objective was to explore the production of protective devices through 3D printing, both for the maxillofacial area and other parts of athletes’ bodies.”
Case Study: Maxillofacial Protective Mask
The heart of the thesis is represented by the Case Study, in which Gallozzi,student
of Mechanical Engineering at the Università Politecnica delle Marche, collaborated with our company in the development of a maxillofacial protective mask designed for soccer players.
Material and Printing Technology Selection:
The first step involved choosing the most suitable material and printing technology for the application.
In this case, the chosen material is PA603CF, a composite of PA2200 loaded with carbon fiber.
Its ability to provide high-performance, coupled with its resistance to the stresses typical of the soccer environment, makes it ideal for the production of advanced protective devices.
The selected printing technology is SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), enabling the precise and durable printing of PA603CF parts.
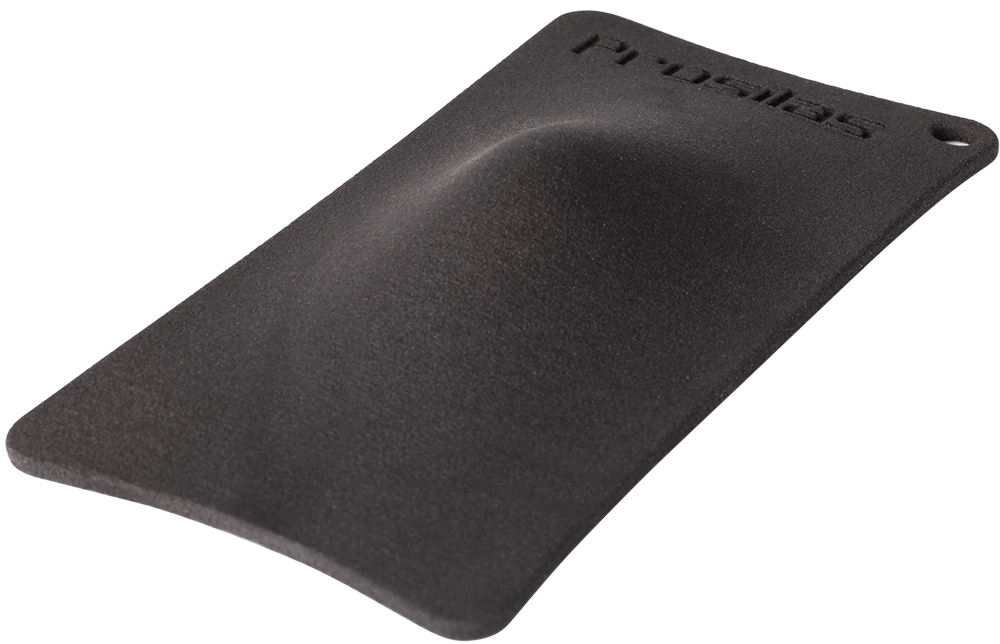

PA 603 CF – Carbon filled Polyamide
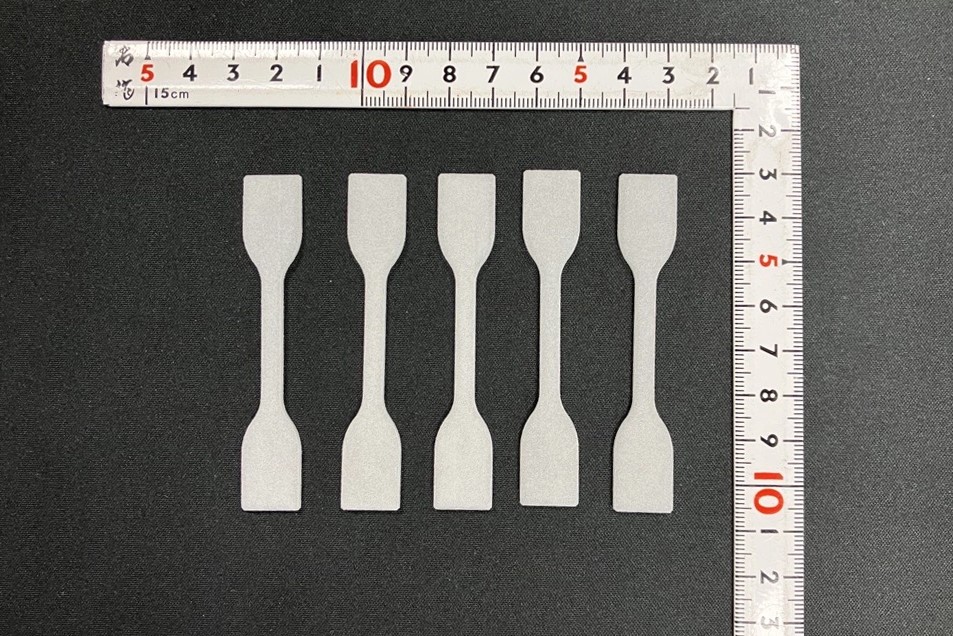
Exemple of specimens for tensile and flexural tests
Design and Production Workflow
1 – Modeling and Printing of Specimens for Tensile and Flexural Testing:
Prior to the production of the mask, validation tests of the material were conducted, in accordance with UNI EN ISO 527-2, 1A, and ISO 178 standards.
The specimens modeled using Siemens NX passed tensile and flexural tests, confirming the suitability of PA603CF for the maxillofacial protective mask.
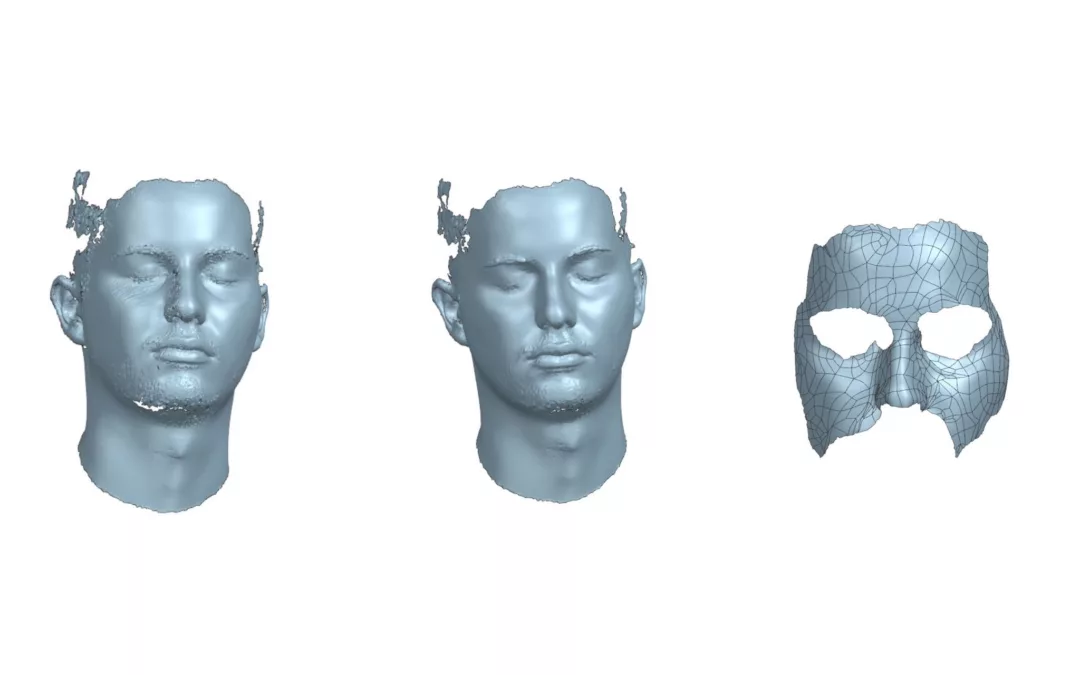
2 -Face scanning:
The next phase involves the 3D scanning of the subject’s face for whom the mask has been modeled.
This scanning is performed using a 3D scanner, which captures the shape and size data of the face.
The acquired data is then used to create a 3D model of the mask that perfectly fits the subject’s face using reverse engineering techniques
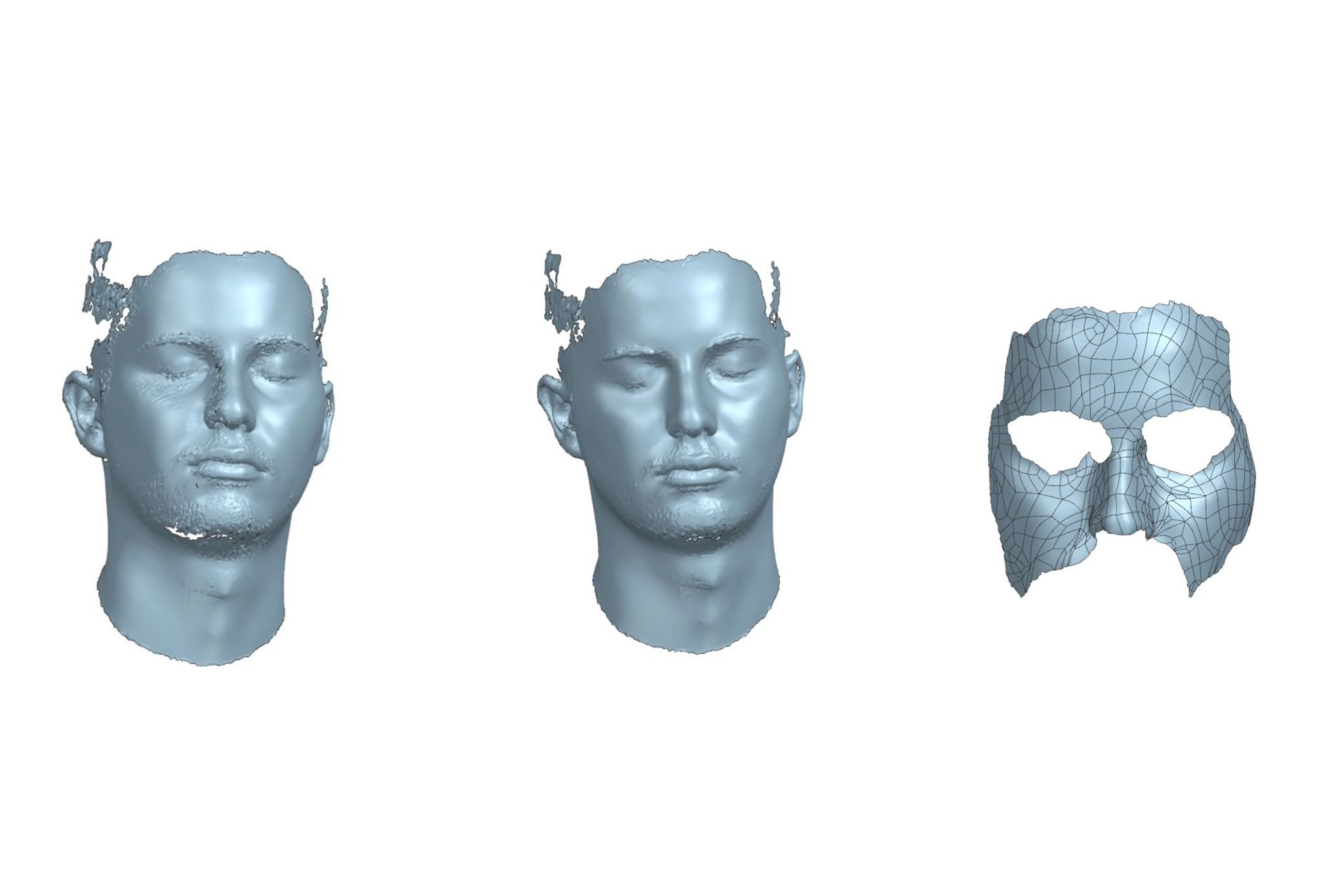


Scanning phases

Mask 3D model
3 – 3D Modeling:
The 3D model of the mask is created using Siemens NX, a 3D modeling software. The model is designed to protect the most vulnerable areas of the face, such as the cheekbone, jaw, and nose.
Consideration for comfort and lightness was crucial, along with the desire to preserve the athlete’s peripheral field of vision to the maximum extent possible.
4 -Prima realizzazione del prototipo
Prima di procedere con la maschera finale, è stato creato un prototipo in VeroWhitePlus con la stampante 3D Objet30 di Stratasys, che sfrutta la tecnologia di material jetting.
Questo passo preliminare ha consentito di valutare la bontà del design prima di passare alla fase successiva.
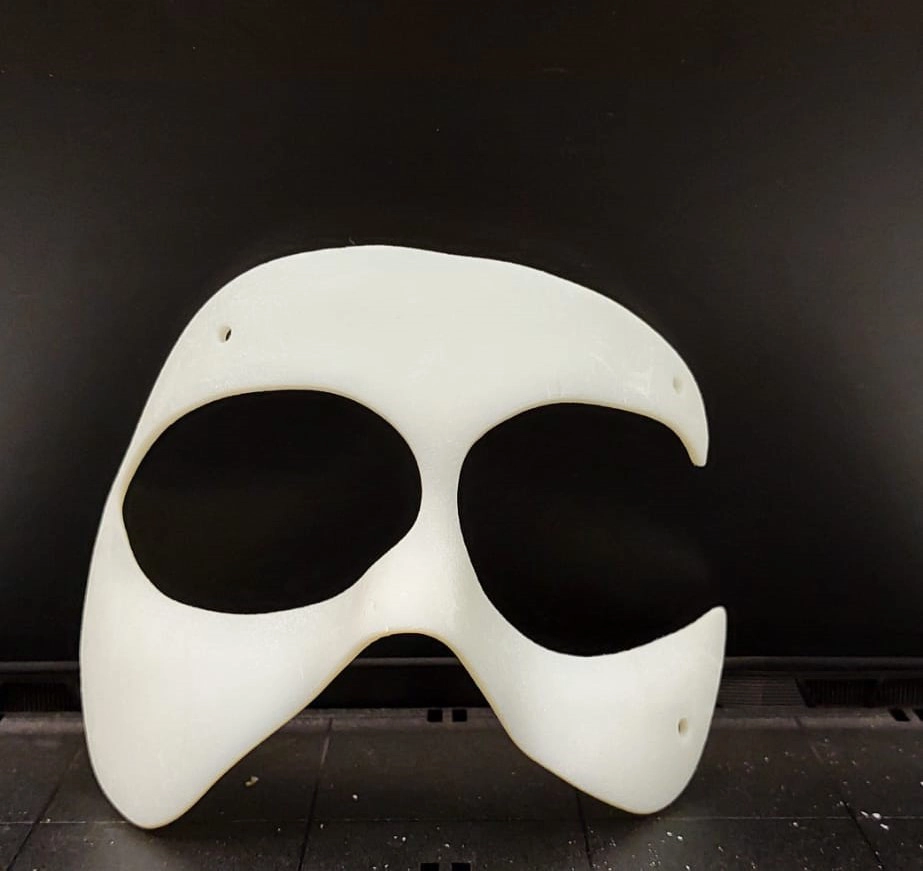

First protoype of the mask

Last phase, finally the mask is printed
5 –3D Printing with SLS Technology and PA603CF Material
Once the success of the prototype was confirmed, the 3D printing of the final protective mask in PA603CF was initiated using our company’s SLS 3D printers.
This phase represents the culmination of the thesis work, with the chosen material selected for its intrinsic properties of rigidity, strength, hardness, and lightness.
Post-Printing Phases: Safety and Customization
Simone Gallozzi theoretically discussed post-printing phases, including the need to internally coat the mask with a soft material for skin contact. He proposed the use of strategic supports to avoid contact with the traumatized area.
Surface treatments and aesthetic customizations are considered to enhance the appearance of the mask, completing the process with the addition of elastic bands through designated holes.
Simone Gallozzi’s work represents a very interesting application of Additive Manufacturing in the world of sports, highlighting how collaboration between academia and industry can open new perspectives for innovation.